Article not found
This article is no longer available. But don't worry—we've gathered other articles that discuss the same topic.
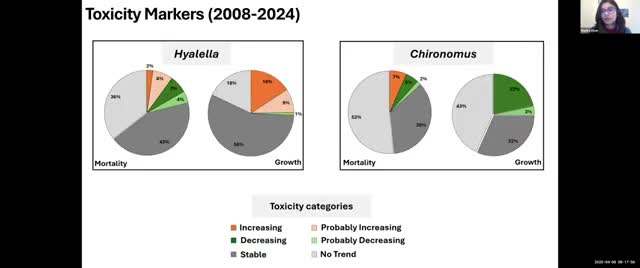
SPOT review: toxicity screening highlights some persistently impacted sites, multiple endpoints add value

UC Davis researchers outline how non‑targeted analysis can augment SPOT monitoring
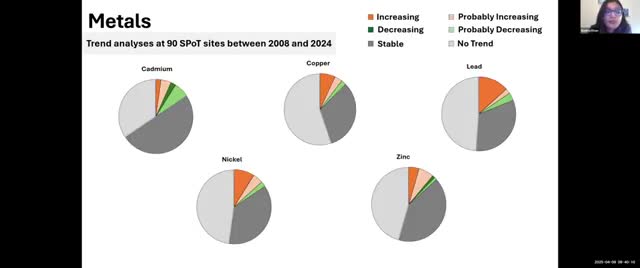
SPOT program: PFAS detected widely at urban tier‑2 sites, but trends need more years of data

