AI Revolutionizes Healthcare Amidst Regulatory Challenges
August 23, 2024 | Medical Board of California, Other State Agencies, Executive, California
This article was created by AI summarizing key points discussed. AI makes mistakes, so for full details and context, please refer to the video of the full meeting. Please report any errors so we can fix them. Report an error »
In a recent government meeting, discussions centered around the implications of artificial intelligence (AI) in various sectors, particularly healthcare, and the pressing need for regulatory frameworks to ensure ethical use and consumer protection.
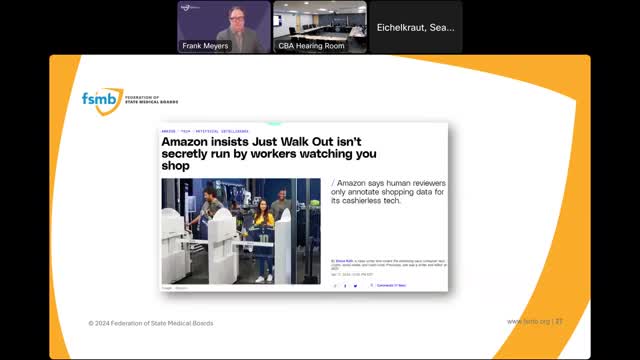
One of the key topics was the public's misunderstanding of AI technologies, exemplified by Amazon's automated checkout system. While the system relies on cameras and AI to track purchases, it was revealed that human annotators play a crucial role in correcting errors and training the models. This highlights the importance of transparency and consent regarding AI's operational mechanisms.
The meeting also showcased advancements in AI diagnostics, such as the FDA-approved Luminex Core, which autonomously diagnoses diabetic retinopathy without human intervention. Other notable applications include AI tools that assist in diagnosing brain tumors during surgery and enhance the accuracy of colonoscopies, significantly reducing error rates. These innovations raise critical questions about the evolving standards of care and the potential necessity of AI in medical practices.
However, the discussion underscored a significant regulatory gap in the United States compared to the European Union, which has implemented the EU AI Act. This comprehensive legislation mandates transparency and data training requirements for AI systems. In contrast, U.S. federal efforts remain fragmented, with only executive orders and existing laws providing limited oversight.
State-level initiatives, such as Utah's Senate Bill 149 and Colorado's Senate Bill 24205, aim to protect consumers while fostering innovation. These bills emphasize disclosure and risk management for AI systems, particularly in healthcare settings. California's proposed Senate Bill 1047, which seeks to impose stringent responsibilities on AI developers, has garnered attention but remains under debate.
The consensus among meeting participants was clear: while state regulations are a step forward, a cohesive federal framework is essential to address the complexities of AI technologies across industries. The need for comprehensive legislation is critical to prevent a disjointed regulatory landscape that could hinder innovation and consumer safety. The Federation's commitment to navigating the ethical incorporation of AI in clinical practice was also highlighted, emphasizing the importance of responsible AI deployment in healthcare.
One of the key topics was the public's misunderstanding of AI technologies, exemplified by Amazon's automated checkout system. While the system relies on cameras and AI to track purchases, it was revealed that human annotators play a crucial role in correcting errors and training the models. This highlights the importance of transparency and consent regarding AI's operational mechanisms.
The meeting also showcased advancements in AI diagnostics, such as the FDA-approved Luminex Core, which autonomously diagnoses diabetic retinopathy without human intervention. Other notable applications include AI tools that assist in diagnosing brain tumors during surgery and enhance the accuracy of colonoscopies, significantly reducing error rates. These innovations raise critical questions about the evolving standards of care and the potential necessity of AI in medical practices.
However, the discussion underscored a significant regulatory gap in the United States compared to the European Union, which has implemented the EU AI Act. This comprehensive legislation mandates transparency and data training requirements for AI systems. In contrast, U.S. federal efforts remain fragmented, with only executive orders and existing laws providing limited oversight.
State-level initiatives, such as Utah's Senate Bill 149 and Colorado's Senate Bill 24205, aim to protect consumers while fostering innovation. These bills emphasize disclosure and risk management for AI systems, particularly in healthcare settings. California's proposed Senate Bill 1047, which seeks to impose stringent responsibilities on AI developers, has garnered attention but remains under debate.
The consensus among meeting participants was clear: while state regulations are a step forward, a cohesive federal framework is essential to address the complexities of AI technologies across industries. The need for comprehensive legislation is critical to prevent a disjointed regulatory landscape that could hinder innovation and consumer safety. The Federation's commitment to navigating the ethical incorporation of AI in clinical practice was also highlighted, emphasizing the importance of responsible AI deployment in healthcare.
View full meeting
This article is based on a recent meeting—watch the full video and explore the complete transcript for deeper insights into the discussion.
View full meeting